
Getty Images/iStockphoto
How does DMARC affect email marketing?
Marketers must prepare for DMARC to ensure their emails reach customers' inboxes -- rather than their spam or junk folders -- and to build trust between consumers and the brand.
Email marketing remains a cornerstone of digital marketing strategies, and brands must maintain the integrity and trustworthiness of email communications to benefit their reputations and future revenues.
This is where Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance comes into play. DMARC is a security tool, but it can also help marketers ensure their audiences receive and trust their email campaigns.
Consumers aren't always aware if an email is legitimate or not, so many major email providers now require businesses to implement DMARC in their email programs. In late 2023, Google and Yahoo both announced they would require all bulk senders to have DMARC by early 2024. Both brands recognize the importance of email as a communication method for bulk senders and are taking appropriate steps to reduce unwanted spam and bad actors from reaching users.
Explore what DMARC is, how it works, its benefits for email marketing and essential steps that teams can take to implement DMARC effectively.
What is DMARC?
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that enables domain owners to protect their domain from unauthorized use, commonly known as spoofing. If domain owners can specify which mechanisms to employ to authenticate their mail, such as DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) and Sender Policy Framework (SPF), they can create a safer email environment.
When a receiving mail server gets an email, it checks the DMARC record of the sender's domain to determine if the message is authentic or spoofed. If it passes the DMARC check, the email is more likely to reach the recipient's inbox. This process enhances email deliverability and helps maintain a brand's reputation.
Marketers should also understand DMARC's relationship with other protocols, like DKIM and SPF. While SPF verifies that incoming messages come from an authorized server, DKIM lets the receiver check through cryptographic authentication that the domain's owner indeed authorized an email.
DMARC provides a comprehensive approach to email security, as it enables domain owners to set policies to handle mail that fails authentication. Messages that don't pass DMARC alignment aren't delivered to the recipient's inbox. These include messages sent directly from an organization or on behalf of third-party email service providers, such as HubSpot, Mailchimp, Constant Contact and others.
How DMARC works
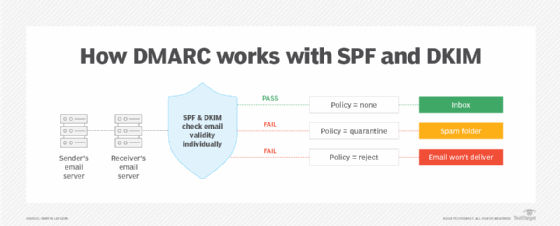
DMARC aligns the SPF and DKIM protocols to verify an email's authenticity. The process works as follows:
- SPF check. This checks if the email comes from an IP address authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain.
- DKIM check. This verifies the digital signature of the email, which confirms the content of the email wasn't altered during transit.
- Alignment check. DMARC checks the domain in the From header aligns with the domains verified by SPF and DKIM.
- Policy application. Based on the DMARC policy -- the results of which are None, Quarantine or Reject -- the receiving server decides what to do with emails that fail these checks.
- Reporting. DMARC provides feedback to the domain owner about emails that pass or fail authentication checks, helping identify potential abuse.
Benefits of DMARC
Implementing DMARC offers advantages that significantly enhance email security and reliability for organizations. DMARC ensures the authenticity of emails, protects against phishing attacks, improves email deliverability and strengthens regulatory compliance.
Collectively, these benefits build trust with customers and safeguard sensitive information, making DMARC vital to any email marketing strategy.
1. Protection from phishing attacks
Cybercriminals commonly use phishing to deceive consumers into providing sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card numbers. DMARC ensures that emails claiming to be from legitimate brands are indeed from those brands to prevent phishing attacks. When consumers receive emails that pass DMARC checks, they can have greater confidence the messages are authentic.
2. Enhanced trust in communications
Consumers and businesses of all sorts, including financial institutions, healthcare providers and retail companies, often rely on email for important communications. When organizations implement DMARC, they can ensure emails to consumers are legitimate. This protection builds trust between consumers and the brand, which can enhance overall CX.
3. Reduced risk of identity theft
DMARC prevents email spoofing, so it also reduces the risk of identity theft for consumers. Spoofed emails can trick recipients into sharing personal information or clicking on malicious links that lead to malware infections. With DMARC, the likelihood of those emails reaching consumers' inboxes lowers, and it better safeguards their personal information.
This practice can also reduce customer churn and encourage repeat purchases from consumers, as they can gain more trust in the brand.
4. Compliance with regulatory standards
Organizations are under a lot of pressure to protect user data, as consumers benefit when businesses comply with data protection regulations, like GDPR and CCPA. DMARC helps organizations meet these regulatory requirements, as it secures email communications and protects consumer data. This compliance also offers consumers an added layer of security and peace of mind regarding the handling of their personal information.
5. Improved email deliverability
Emails that fail authentication checks are often sent to spam or junk folders, causing consumers to miss important communications. With DMARC, authenticated emails are more likely to reach inboxes, so customers receive timely and relevant information from brands they trust. This process improves the overall efficiency and reliability of email communications.
6. Increased awareness and education
DMARC implementation often comes with efforts from businesses to inform consumers about email security and how to recognize legitimate emails. This increased awareness helps consumers become more vigilant and knowledgeable about online threats, so they can further enhance their online security and strengthen their trust in their go-to brands.
7. Insights through reporting
DMARC's reporting feature offers detailed insights into email traffic, helping both businesses and consumers understand the landscape of their email ecosystem. For businesses, these reports include critical data on the sources and authentication of emails sent using their domain. This visibility enables organizations to identify unauthorized email use, detect potential threats, fine-tune their authentication policies and refine email marketing strategies.
How to implement DMARC for email marketing
Implementing DMARC can seem daunting, but the following steps can ensure its smooth integration into an email marketing strategy.
1. Ensure SPF and DKIM are set up
Before implementing DMARC, SPF and DKIM should be in place. These protocols form the foundation of DMARC and are necessary for its proper functioning:
- SPF setup. Define the authorized IP addresses to send emails on behalf of the company domain.
- DKIM setup. Add a digital signature to emails, which receiving servers can verify to ensure bad actors didn't tamper with the email.
2. Define DMARC on the company's DNS
Add a DMARC record to the organization's DNS settings, which specifies how to handle emails if they fail SPF or DKIM checks. The policy can be set to the following statuses:
- None. The DMARC policy monitors the messages but doesn't take action. The emails reach their targets, and the sending server receives reports on them. This is typically just used for testing.
- Quarantine. Suspicious emails go to the spam or junk folder.
- Reject. The receiving server completely rejects and blocks the emails.
3. Start with a monitoring policy
Begin with a None policy to monitor how DMARC affects email flows without affecting delivery. Analyze the reports generated to understand how the DMARC policy processes the emails.
4. Analyze DMARC reports
DMARC offers regular reports that detail the emails' authentication statuses. Use these reports to identify and resolve issues with the email authentication setup. Look for patterns of unauthorized use, and adjust policies accordingly.
5. Gradually adopt Quarantine and Reject policies
Once confident that legitimate emails pass authentication checks, gradually move to stricter policies -- Quarantine or Reject -- to protect the domain from unauthorized use. This staged approach helps avoid disruption in email delivery.
6. Educate internal teams
Ensure all customer-facing teams, like marketing, and IT team members understand DMARC and its relevance to email marketing. This collective awareness fosters a culture of security throughout the organization.
7. Continuously monitor and update policies
DMARC implementation is not a one-time task. Continuously monitor the reports, and update policies as needed based on changing email threats and to ensure ongoing email security.
If marketers understand and properly implement DMARC, they can significantly enhance the security and effectiveness of their email marketing strategies. DMARC protects customers from phishing, ensures compliance with regulatory standards, improves email deliverability and builds brand trust. As email threats continue to evolve, DMARC remains a critical tool in the marketer's arsenal to maintain secure and effective communication.
Griffin LaFleur is a MarketingOps and RevOps professional working for Swing Education. Throughout his career, LaFleur has also worked at agencies and independently as a B2B sales and marketing consultant.





